Start with NEMA standards, then consider other conditions.
Attabox
06/14/2018
Enclosure selection for pump systems is often at the bottom of the list when it comes to addressing design or redesign. Yet choosing the wrong enclosure due to a lack of education could become a costly mistake down the road, especially if the specified enclosure fails. This type of failure can result in a lawsuit or the loss of a good customer. Making sure that enclosure choices are well thought out is always in a company’s best interest. When choosing enclosures, it is best to research all the available materials and current rating standards. Plus, users should consider the environment where the enclosure will be placed.
Materials Available for Electrical Component Protection
Enclosures can be made from metallic or nonmetallic material, but the material must serve its function of protection for the life of the installation. Durability and longevity are key. There are three typical types of materials available: thermoset composites, metal and thermoplastics. Thermoset materials, such as a polyester resin combined with glass, create a unique composite fiberglass reinforced polyester (FRP) that is exceptionally durable and weather resistant. Like thermoplastics, FRP provides a greater degree of corrosion resistance than painted stainless steel, yet will perform better than metal and plastics in extremely harsh environments. Metal: The Basics Common metal enclosure choices included carbon steel, stainless steel and aluminum, with carbon steel being the most prominent choice based on its low initial cost. Carbon steel is typically galvanized or painted to prolong the service life. Premium metals such as stainless steel and aluminum are used where long life, corrosion resistance and weatherability are critical, such as protecting controls for junction boxes in applications. Thermoplastics: The Basics Thermoplastics—such as polycarbonate, polyester, acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC)—offer a degree of corrosion protection beyond painted carbon steel. Thermoplastics are more susceptible to ultraviolet (UV) exposure and weathering degradation over time. Certain stabilizers are now added to extend the life of the enclosure, but ultimately, the nature of the thermoplastics will yield to extended weathering.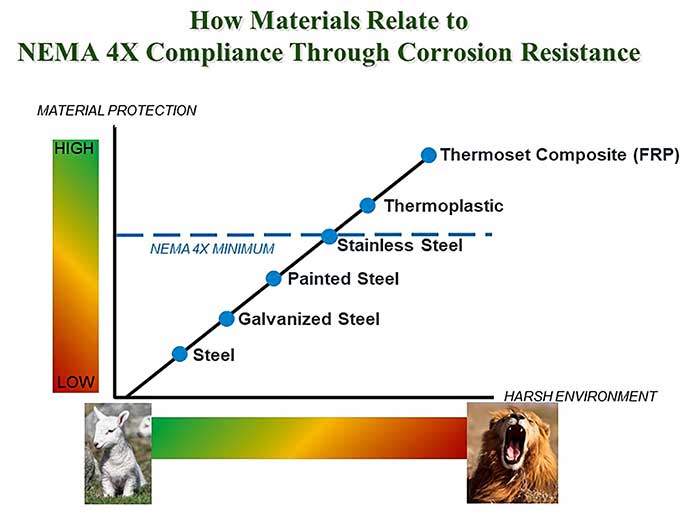 Image 1. Corrosion resistance of various materials (Images courtesy of Attabox)
Image 1. Corrosion resistance of various materials (Images courtesy of Attabox)Influential Factors to Reduce the Failure of Enclosures
Often trade-offs between performance, acquisition cost and life cycle cost are made in the process to find the ultimate choice for a unique application. Consider these factors that influence the enclosure specification for applications and how each type of enclosure might stack up:- environmental considerations
- standards requirements
- physical characteristics
- electrical characteristics
- thermal management
- condensation
- cost solutions
Environment Conditions: Special Considerations
Another factor that must be considered is how resistant the enclosure must be. Some factors to consider are:- corrosion and chemical resistance—especially when exposed to chlorine or acid
- flammability—understand Underwriters Laboratory (UL) 94-5VA or nonhalogenated options
- safety—nonconductive or will you need modifications to secure controls
- impact resistance—consider looking into modulus of elasticity ASTM D638
- sunlight, UV resistance—ask enclosure manufacturers to inform you of their UV protection available
- appearance—the finish or color choices; many new options for color are available
 Image 2. Users should consider materials, rating standards and environment when choosing an enclosure.
Image 2. Users should consider materials, rating standards and environment when choosing an enclosure.
