To optimize system operation, designers must match the conditions that encompass the system curve.
08/16/2016
 Image 1. Process and maintenance engineers should review the pumping system design in the event of a process change. (Image and graphic courtesy of Sulzer)
Image 1. Process and maintenance engineers should review the pumping system design in the event of a process change. (Image and graphic courtesy of Sulzer)Failure at Shutoff Flow
This concept can be illustrated by a recent repair project. A multistage boiler feed pump was brought to a service center for repair, and it was immediately clear that the pump had suffered severe damage. An initial inspection showed that the suction-side seal, several impellers, sleeves and stationary components had been destroyed. The evidence indicated that the pump had operated at or near shutoff flow. When a pump operates in a boiler feed system, iron oxide deposits are often found in the casing. In this example, the deposits were absent in the first three stages of the pump but intact on the latter stages. This indicated that the pump had experienced a condition where the input energy from the impellers had turned the water to steam before it had a chance to exit the pump. The presence of steam in a pump is a violent condition that induces vibrations and can lead to surface erosion. Normally, the frictional losses in a pump are converted to a few degrees of heat and discharged in the water flow. With very low or no flow, this energy builds in the pump. Eventually, the heat input to the liquid builds to an amount that surpasses its vapor pressure and it becomes two phases—liquid and gas. As the input of energy increases, the liquid heats to the point of transformation and turns completely into the gas phase. Operating a pump under these circumstances is inefficient, and operators should take steps to properly assess the minimum flow requirements of an installation and perform remedial work to indicate when this condition is not being met.Causes of Failure
The possible causes of the pump failure were reviewed with the plant owner who was keen to avoid similar cases. A number of issues were highlighted, including a misunderstanding of the required flow rate of the pump. The plant bases calculations mainly on steam rates, so these were converted to water flows and plotted on the pump operating curve. This established that the pump was operating close to the minimum flow point and that its pump operating curve was fairly flat at the lower flow region.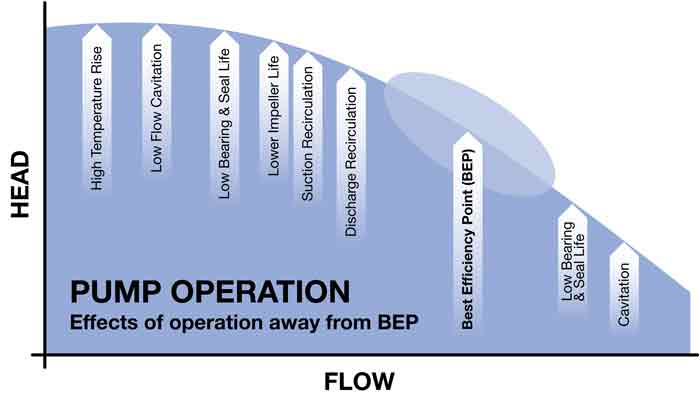 Figure 1. It is important to understand the consequences of dialing back pump flows and the effects on reliability.
Figure 1. It is important to understand the consequences of dialing back pump flows and the effects on reliability. Image 2. The refurbishment process requires attention to detail for the best results.
Image 2. The refurbishment process requires attention to detail for the best results. 
