The world of industrial pumping moves billions of gallons daily, powering industries and delivering solutions for complex challenges. Each application demands precision and reliability, making the choice of pump technology crucial. This article explores the foundational differences between positive displacement (PD) pumps and rotodynamic pumps.
The Basics of Pump Technology
Industrial pumps can be broadly categorized into two main types: PD pumps and rotodynamic pumps. While rotodynamic pumps rely on velocity to move fluid, PD pumps operate by capturing a fixed volume of fluid and moving it from the pump inlet to the pump discharge connection. This fundamental difference shapes their respective performance characteristics and suitability for various applications.
PD pumps are designed to deliver consistent flow regardless of backpressure, making them highly reliable in demanding conditions. This reliability translates into minimized downtime and consistent operations, even in extreme environments. Industries such as oil and gas benefit from uninterrupted production, while food, chemical and pharmaceutical sectors rely on the precision of PD pumps to maintain product integrity and quality standards.
How PD Pumps Work
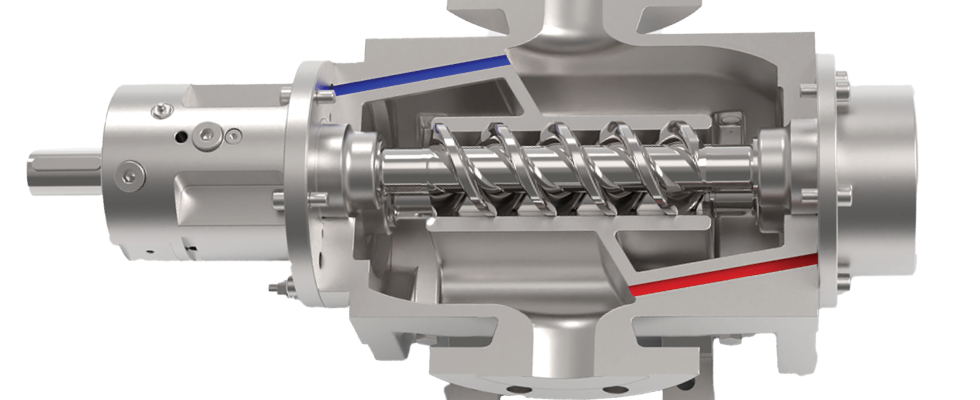
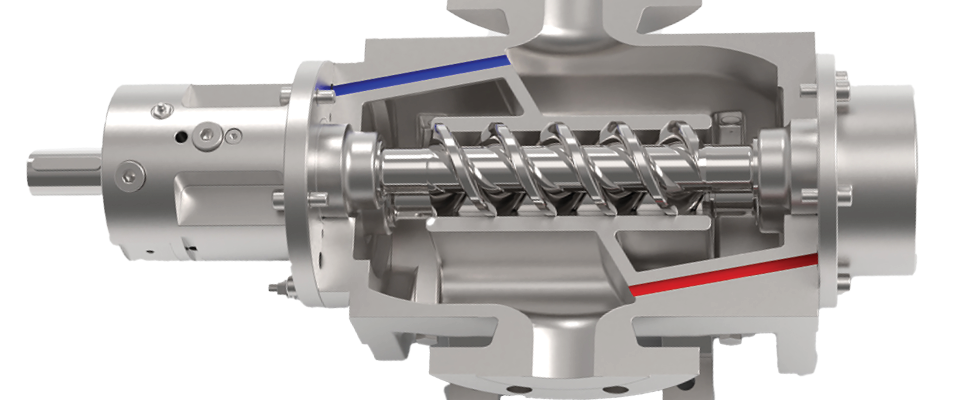
At the core of PD pump operation is a simple yet effective mechanism: capturing and displacing a set volume of fluid. This approach ensures steady flow, predominantly independent of pressure variations. PD pumps are further divided into two main categories:
Rotary pumps: These include screw, gear, lobe and vane pumps, which use rotating elements to move fluid efficiently. They excel in handling high-viscosity fluids and delicate applications requiring minimal shear.
Reciprocating pumps: Plunger, piston and diaphragm pumps use linear motion to displace fluid. These pumps are ideal for high-pressure environments and precise fluid control.
The Advantages of PD Pumps
Pressure-flow characteristics: Rotodynamic pumps depend
on velocity and can suffer reduced flow under higher pressure, but PD pumps can maintain a nearly vertical performance curve. This means their flow remains largely consistent, even as backpressure fluctuates.
Handling viscosity: PD pumps thrive in applications involving high-viscosity fluids. Increased viscosity reduces internal slip—the backflow of fluid—resulting in greater efficiency. Industries handling materials like crude oil, molasses, polyols and slurries benefit significantly from this capability.
Air entrainment and contamination:
PD pumps handle mixed-phase fluids containing air or gas effectively, ensuring consistent performance where other pumps might fail.
Energy efficiency with challenging fluids: The adaptability of PD pumps to various fluid characteristics—including viscosity, contamination and temperature—reduces energy loss, making them a cost-effective choice for complex applications.
Applications of PD Pumps
The versatility of PD pumps makes them indispensable across a range of industries. Here is a deeper look at why PD pumps excel in each application:
Oil and gas: Multiphase pumping, chemical injection and crude oil transfer demand precision and reliability. PD pumps handle varying viscosities and mixed-phase fluids with ease, ensuring consistent flow even under extreme pressures. This makes them a cornerstone in oilfield operations and refining processes.
Food and beverage: PD pumps are crucial for transferring delicate and shear-sensitive products like syrups, yogurts and creams. Their smooth, non-pulsating flow prevents product degradation, ensuring high-quality output in hygienic environments.
Pharmaceuticals: In pharmaceutical applications, PD pumps provide precision dosing and maintain sterility through clean-in-place (CIP) systems. Their ability to handle sensitive and high-viscosity fluids ensures compliance with strict industry standards.
Wastewater treatment: Handling sludge and high-solids-content fluids is a challenge where PD pumps excel. Their durability and ability to maintain consistent performance in abrasive environments make them indispensable for municipal and industrial wastewater facilities.
Positive displacement pumps often excel in scenarios requiring precision, reliability and adaptability. Their ability to maintain consistent flow under varying pressures, handle viscous fluids and operate effectively with mixed-phase materials ensures optimal performance in challenging environments. Rotodynamic pumps remain suitable for high-flow, low-viscosity applications, while PD pumps may be a more efficient option for multiphase flow and higher-viscosity industrial needs.
This foundational understanding sets the stage for a deeper exploration of PD pumps in Part 2, where we will further explore the specific types of PD pumps and address their limitations and best practices.

