Learn which flow, pressure, level and temperature equipment works best in each phase of the process.
Tek-Trol
09/10/2018
Wastewater originates from many sources, including industrial activities, domestic use, various farming and agricultural processes, medical waste and transportation. It refers to water that has been fundamentally changed—usually in fluid quality or composition but also including temperature. But what happens to the water? Everyone has heard of wastewater treatment plants, but what is happening, and how is it accomplished? This article delves into basic principles of wastewater treatment as well as solutions for each process.
Intake & Mechanical Treatment
The wastewater treatment industry requires continuous process measurement systems and control. Most sources of wastewater originate from agricultural, industrial or domestic use. Initially, the goal of wastewater treatment is to remove rough or crude solids and other large containments from raw water. During this initial process (referred to as the grit channel process), the velocity of incoming wastewater is controlled, allowing most of the sand, grit and stones to settle to the bottom of the channel while retaining most of the suspended organic material in the water.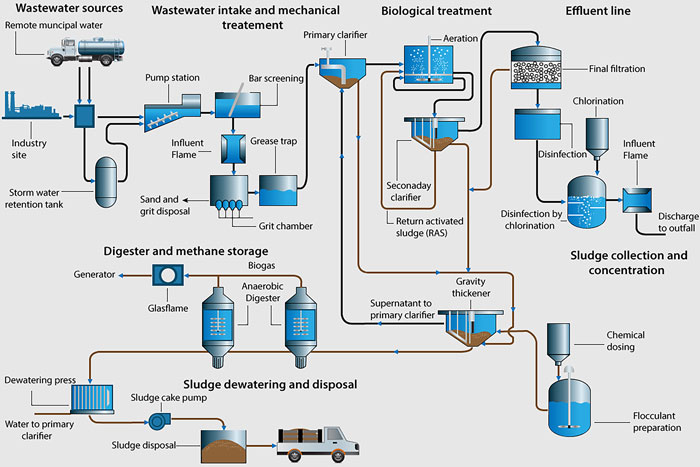 Image 1. How wastewater is treated. Click here to view a larger version of this image. (Image courtesy of Tek-Trol LLC)
Image 1. How wastewater is treated. Click here to view a larger version of this image. (Image courtesy of Tek-Trol LLC)
