With a rise in external pressures like higher energy costs, increased regulations and changing industry standards, the pumping industry is faced with finding creative ways to combat increased life cycle costs of pumping systems. Leveraging modern pumping technologies can help organizations realize cost savings, decrease energy consumption, improve uptime and extend equipment life. Inherent technology in variable frequency drives (VFDs) can enable these benefits. The multipump function onboard VFDs is used in process applications where multiple pumps maintain pressure or flow. A single proportional integral derivative (PID) controller loop in the VFD is used to maintain a process set point, like a fixed frequency reference. If a single pump is not able to meet the demand, additional pumps are used to boost the system. There are two basic types of multipump control: single drive and multiple drive. Multipump control with a single drive uses one drive with one motor and controls up to four more motors running across the line. Multipump control with multiple drives uses one drive per motor through a master/slave control platform with a total of five drives. In both scenarios, the VFD uses the onboard PID loop to execute the logic controls based on the fixed frequency reference.
Cost Savings
System cost can be reduced when the VFD’s onboard multipump control is used. The PID capabilities inherent to the drive eliminate the need for an external programmable logic controller (PLC) to execute the logic. By removing the PLC from the control system, cost savings result from fewer requirements of equipment, labor and engineering.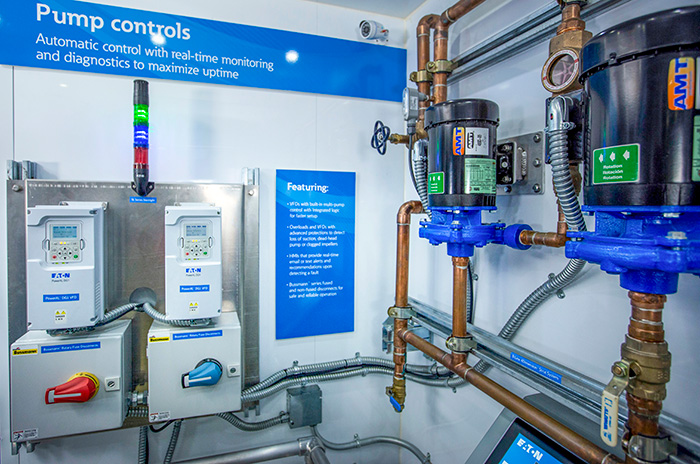 Image 1. Multiple pump controls. (Images courtesy of Eaton)
Image 1. Multiple pump controls. (Images courtesy of Eaton)Energy Savings
While the single-drive solution requires a lower upfront cost due to the price of drives compared to across the line starters for the downstream pumps, greater energy savings are typically realized with the multiple drives solution through inherent energy savings in VFDs for each motor. Furthermore, enabling the onboard energy optimization algorithm on VFDs reduces energy consumption by an additional 2 to 10 percent per motor compared to VFDs without the energy optimization algorithm enabled.Improved Uptime
Using multiple pumps to meet a process demand such as flow or pressure impacts system performance and uptime. Properly sizing multiple motors to collectively meet the pressure demand provides redundancy in the pumping system. Using a VFD’s onboard PID loop to control the pumps’ response to the pressure demand builds in redundancy. Suppose a system is sized to use three smaller pumps instead of one larger one to meet the pressure demand. In the event that one of the pumps fails, the drive sends signals to the other two pumps to increase speed and maintain constant pressure, never forcing the system to go offline, despite a pump failure.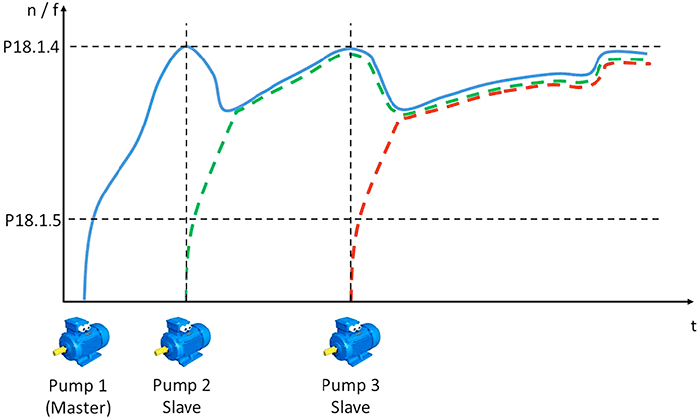 Image 2. Multidrive/multipump control curve (speed).
Image 2. Multidrive/multipump control curve (speed).
