These systems can increase efficiency and add unique insight.
Schneider Electric
03/21/2017
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is a business buzzword. But asking 10 people for a definition of IIoT will likely result in 10 different answers. Additionally, many may think IIoT refers to connecting people with machines, instead of a connected process. This concept goes beyond basic process management to informing and educating people on what is happening in a process. Further, some people who mention machines often think of industrial applications, such as packaging or conveying equipment. Pumping systems and pumping applications are often left out of the discussion.
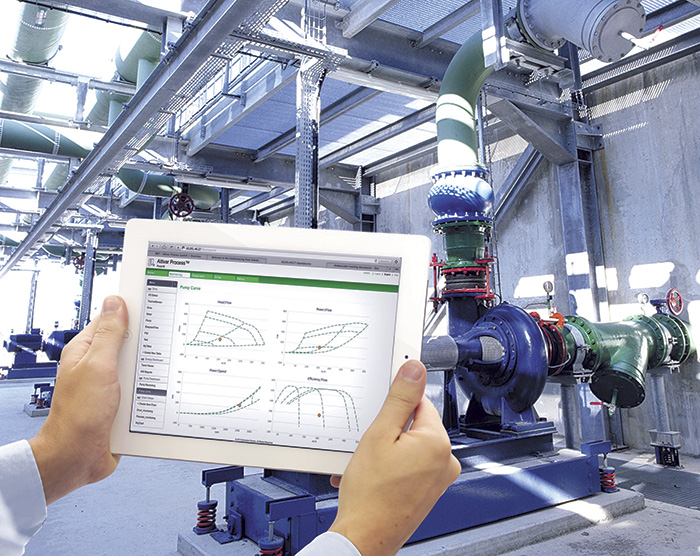 Image 1. Tracking pump output levels through a browser-based monitoring application for variable frequency drives using a handheld device (Image and graphics courtesy of Schneider Electric)
Image 1. Tracking pump output levels through a browser-based monitoring application for variable frequency drives using a handheld device (Image and graphics courtesy of Schneider Electric)Evolution, Not Revolution
The IIoT is an “evolution” and not a “revolution.” As with most evolving technologies, adoption curves are impacted by both the technology and operators’ willingness to change. The concept of personal connectivity is widespread—an example being the increasing social networking—but it will be dwarfed short term by connected devices (the Internet of Things), as shown in Figure 1. When the “Industrial” is added to the Internet of Things, it takes that same concept and applies it to an industrial process.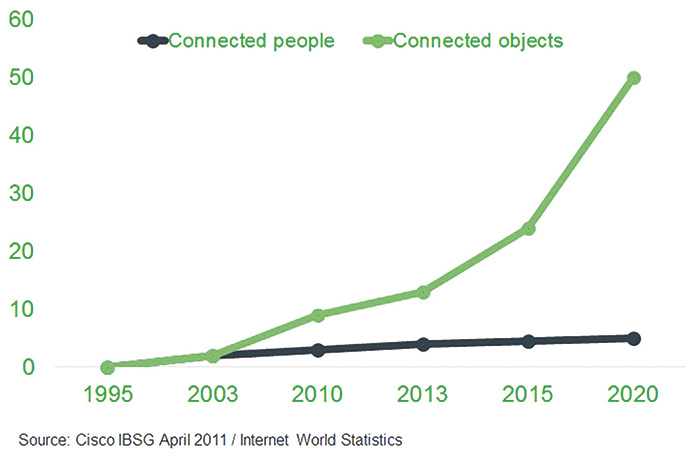 Figure 1. This chart shows that IIoT covers machines and people, with significant growth on the connected-objects front.
Figure 1. This chart shows that IIoT covers machines and people, with significant growth on the connected-objects front.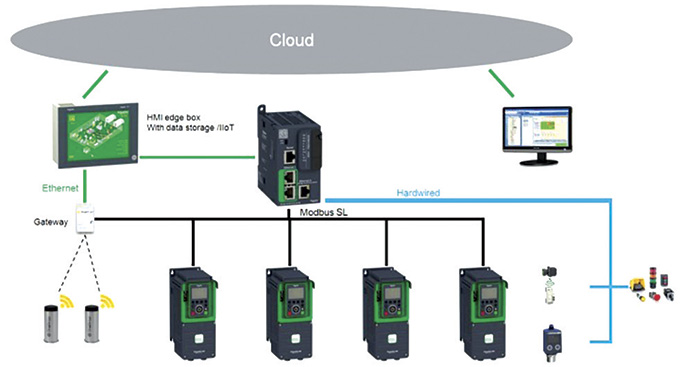 Figure 2. The concept of “smart pumping” combines the technology of each component such as a sensor, variable frequency drive (VFD), programmable logic controller (PLC), human machine interface (HMI), etc., into one smart system.
Figure 2. The concept of “smart pumping” combines the technology of each component such as a sensor, variable frequency drive (VFD), programmable logic controller (PLC), human machine interface (HMI), etc., into one smart system.Remote Connectivity
The IIoT benefits previously mentioned can be seen in many industries. One that is often unique to pumping, however, is connectivity to remote locations. Pumping systems are frequently located in remote locations, which have made monitoring and managing a challenge and expensive. Whether in water/wastewater facilities, oil and gas upstream locations, or commercial buildings, the practicality of local monitoring has been limited. By connecting remote pump stations and systems with a single monitoring system, multiple locations can be monitored from one location. If those stations are part of a larger process, adjustments can be made from that single station that benefit the process as a whole—for example, increasing flow from one pump station to compensate for another, less productive station and ensure even supply. Additionally, remote monitoring in some cases can be done wirelessly through a secure web server. By enabling this capability, a process status can be viewed on an iPad or a mobile phone should the process manager be on the road or unable to make it to a facility because of inclement weather or another reason.System Efficiency
Two upsides of connected solutions involve energy consumption and maintenance. Energy is a crucial consideration because pumps are the primary source of energy savings among motor-driven loads. Maintenance, operations and downtime can account for close to 40 percent of the equipment’s total operation costs. Along with energy consumption, there are several other pump system factors that can be measured or monitored in a smart system. These other factors include the level, flow, pressure, temperature and vibration, among many others. By having insight into these aspects of a pumping system, even greater efficiency can be gained.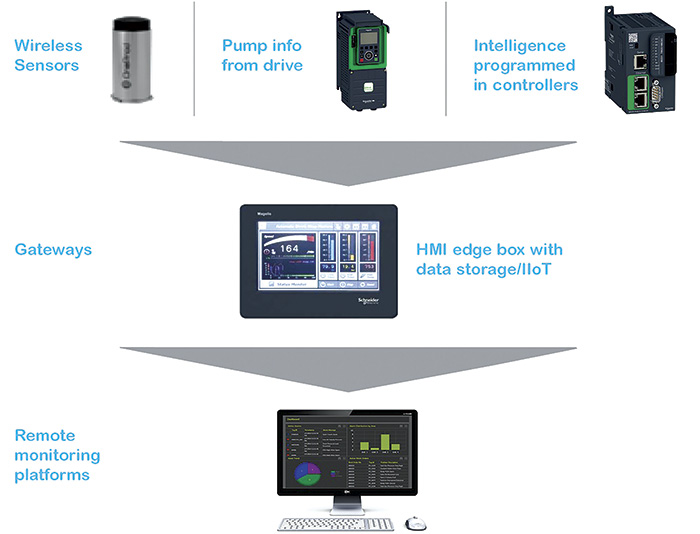 Figure 3. Application data from multiple devices is transmitted and collected for higher system level monitoring.
Figure 3. Application data from multiple devices is transmitted and collected for higher system level monitoring.Practical Benefits
A smart, connected pumping system—the IIoT in pumping—enables a significantly more efficient system by:- Providing insight into individual aspects of a pumping system as well as into how those systems work together for greater overall process knowledge.
- Establishing preventive maintenance plans for systematic inspection to detect potential failures.
- Enabling condition-based maintenance by monitoring pumping system data for an accurate status and risk assessment.
- Deploying corrective maintenance measures as needed in response to an unanticipated problem or emergency.

