
Pumps can be close coupled, rigidly coupled or flexibly coupled to a motor shaft.
- Close coupled pumps have pumping elements attached to an extended motor shaft and therefore do not require alignment when installed in the field.
- Rigidly coupled pumps use couplings that cannot accommodate misalignment; therefore, the alignment is controlled by machined fits between the motor and pump.
- Flexibly coupled pumps use couplings that can accommodate some level of misalignment.
Misalignment (Image 1) can be parallel with respect to the shaft centerlines horizontally and vertically, angular with respect to the shaft centerlines and offset or axial distance between the shafts.
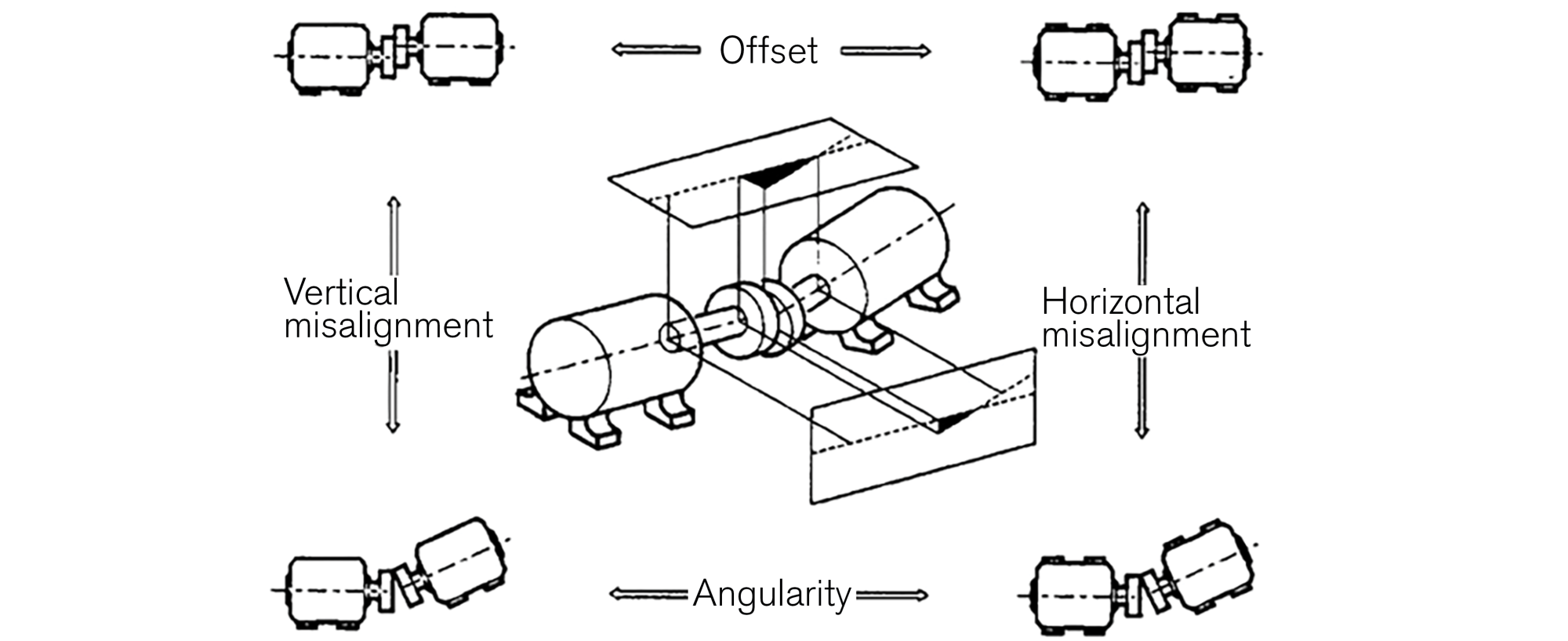
A flexible coupling is used to compensate for minor misalignment of the pump and driver shafts, and the amount of misalignment the flexible coupling can handle will depend on the type. The maximum misalignment for the coupling can be provided by the manufacturer, along with other important factors such as speed and torque capacity.
However, the amount of misalignment acceptable for the coupling will likely be greater than is required by the pump manufacturer. The manufacturer’s installation, operation and maintenance manual should be reviewed to determine the alignment requirement. In general, it is recommended that misalignment is minimized through precision laser alignment tools to reduce cyclic loading applied to the shaft and bearings and to extend the life of the equipment.
For more information on couplings and their capabilities, refer to Couplings for the Pump Industry, second edition, at pumps.org.

