Cost and operational advantages of new direct-drive motor technology have been validated for driving peristaltic pumps. Based on transverse flux innovations, these motors have been used in a variety of high-torque, low-speed applications from conveyors to industrial fans, and recently extended their breadth of operation to include positive displacement pumps. Peristaltic pumps require relatively high torque at low rotational speeds, typically in the range of 5 to 500 rpm, well below the direct-drive capability for incumbent, conventional alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC) motors. As a result, incumbent motors are operated at a higher speed (more than 1,000 rpm), and a speed reduction gearbox is necessary to achieve the required torque and rotational speed. These geared drive systems can be large, heavy and inefficient.
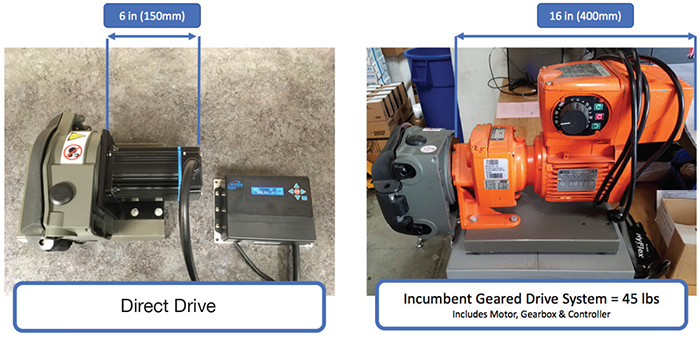 Figure 1. Size and weight comparison: direct drive vs. AC motor with gearbox drive system. (Graphics courtesy of Electric Torque Machines)
Figure 1. Size and weight comparison: direct drive vs. AC motor with gearbox drive system. (Graphics courtesy of Electric Torque Machines)Reducing Mass
The new direct drive motors based on transverse flux technology deliver high continuous torque at low rotational speeds, which eliminates the need for a speed reduction gearbox. This reduces the drive system weight, size, temperature and power consumption of the pump system while offering a wider operating speed range. These motors cover a range of both peristaltic and hose pumps. This transverse flux technology employs increased pole count and low resistance coils, delivering five to 10 times more continuous torque by mass compared to conventional AC or DC motors. In addition, the higher losses in geared drive systems mean the conventional motors need to be oversized to meet the output power requirements. As a result, these drive systems can be priced as much as 50 percent less than geared drive systems.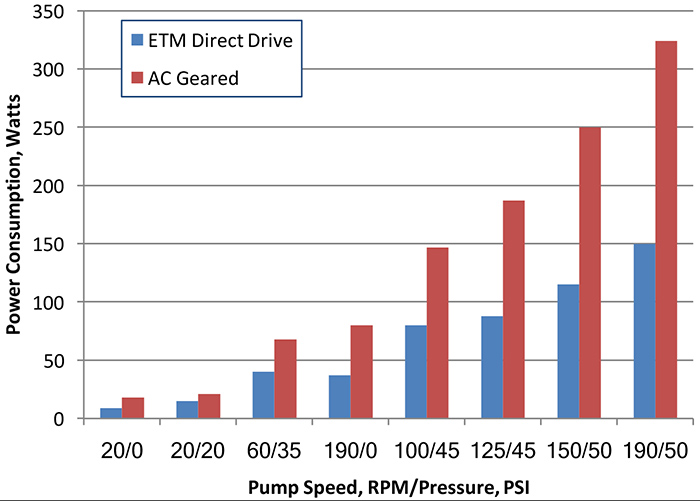 Figure 2. Power consumption comparison showing a 29-54 percent reduction for the direct drive system.
Figure 2. Power consumption comparison showing a 29-54 percent reduction for the direct drive system.
