Working with chemicals can pose a host of dangers. Those in the process industries must take every step possible to protect employees and others from hazardous conditions. The U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) issues and enforces standards designed to increase worker safety, including for facilities that process chemicals. Other countries have similar programs, and the United Nations oversees the Globally Harmonized System for Hazard Communication in an effort to protect workers internationally. One mandated OSHA standard is the Process Safety Management (PSM) of Highly Hazardous Chemicals (standard, 29 CFR1910.119) to prevent the unwanted release of hazardous chemicals that could cause serious exposure. The PSM program requires a systematic approach for evaluating process design, process technology, operations, maintenance and emergency preparedness plans. The program also mandates the implementation of an employee-training program. A properly conducted PSM is a team effort in which the company and employees work together to develop the necessary expertise, experience, judgment and proactive initiative to implement the plan. Since many of the hazardous chemicals covered under a PSM are in either a liquid or gaseous state, possessing a clear picture of all the elements in a piping system is a key point in determining the plan’s success. The requirements of the PSM plan state that the employer provide written instructions detailing the methods in which they will design, operate and maintain the plant to minimize the inadvertent release of highly hazardous chemicals. This article describes how commercially available fluid piping software can be an integral tool in developing and implementing a successful PSM program.
Piping System Model
Piping software can create a piping system model that contains a wealth of information and detailed specifics about each element in the piping system. The information in the model is used by the software’s calculation engine to simulate the operation of the total system. The simulation calculates the flow rates and pressures showing the interaction of the tanks, vessels, pumps, components and controls. It provides a clear picture of how the process piping system operates under any expected condition. To maximize the value of the piping system model as a simulation tool, the following features are included.Visualization
A piping schematic is the primary interface used by the piping system model. The piping schematic has the look and feel of a process flow diagram showing the major items in the system along with of the interconnecting pipelines (See Image 1). Each item on the schematic displays a unique plant equipment identifier, and a variety of symbol shapes are available to choose from, increasing the presentation value of the piping schematic.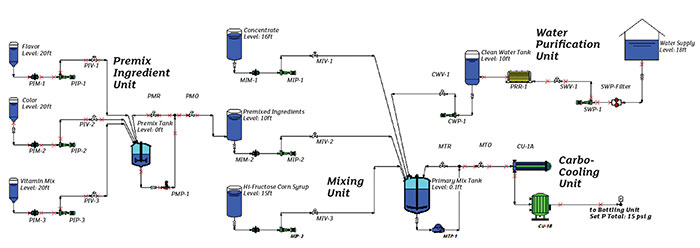 Image 1. The piping schematic shows each element in the system, along with the interconnecting pipelines. It has the look of a typical piping schematic, but it shows how the total system operates. (Image courtesy of the author)
Image 1. The piping schematic shows each element in the system, along with the interconnecting pipelines. It has the look of a typical piping schematic, but it shows how the total system operates. (Image courtesy of the author)
