Q. What methods are recommended for measuring a controlled-volume metering pump's flow rate, and what should be taken into account to ensure an accurate measurement? A. The following methods can be used to measure flow rate for a controlled-volume metering pump. 1. Rate-of-flow measurement by weight: Measurement of rate of flow by weight depends on the accuracy of the scales used and the accuracy of the measurement of time. A certification of scale calibration should be part of the test record, or, in the absence of certification, the scales should be calibrated with standard weights before or after the test. Time intervals for the collection period must be measured to an accuracy of one-quarter of 1 percent. 2. Rate-of-flow measurement by volume: This method involves measuring the change in the volume of a tank or reservoir during a measured period of time. The tank or reservoir can be positioned on the inlet or discharge side of the pump as long as all flow into or out of the tank or reservoir passes through the pump. When establishing reservoir volume by linear measurements, users should consider the geometric regularity (flatness, parallelism, roundness, etc.) of the reservoir surfaces as well as dimensional changes resulting from thermal expansion or contraction, or distortion resulting from hydrostatic pressure of the liquid. Liquid levels should be measured using hook gauges, floats, and vertical or inclined gauge glasses. Under some circumstances, evaporation and loss of liquid by spray may be significant and have a greater effect than thermal expansion or contraction. Users should either allow for such loss or prevent the loss altogether. 3. Rate-of-flow measurement by direct reading meters: For this method, the only suitable meters are direct read devices such as paddle meters, magnetic flow meters and other accepted process measurement instruments. Table 1 shows acceptable fluctuations of test readings and instrument accuracy.
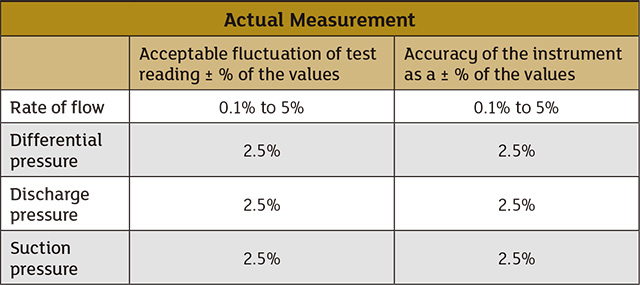 Table 1. Test reading fluctuation and instrument accuracy (Courtesy of Hydraulic Institute)
Table 1. Test reading fluctuation and instrument accuracy (Courtesy of Hydraulic Institute)
