This design overcomes the challenges of exploring and extracting valuable resources.
02/15/2016
The challenges to creating a successful mining operation—whether digging for gold, cement, coal, petroleum products or salt—are both daunting and numerous. Specifically, the technological challenges run a wide gamut:
- Material handling: This requires reliable and highly efficient equipment that needs minimal maintenance and can operate in production areas that require frequent blasting to free ore.
- Processing: Equipment must deal with crushing and grinding rock, as well as the leaching and flotation of complex or difficult-to-treat ores.
- Environmental issues/waste management: Mine operators must have systems that will adequately handle and remove tailings, waste rocks and leach piles. They must also control acid drainage and heavy-metal releases to prevent damage to surrounding freshwater and groundwater supplies.
- Water management: Operators have been working to identify sources of water supply during the extraction process to avoid competing with other industries (such as agriculture and manufacturing) for this precious resource. One alternative is using saline water that comes from the ocean or underground sources. Saline water, however, can mean a high wear rate on equipment.
- Safety: Only equipment certified for use in explosive atmospheres and with potentially hazardous products can be reliably and safely used in mining operations.
The Big Squeeze
The operational characteristics of peristaltic pumps have remained basically unchanged for nearly 140 years. The pump\'92s operation uses alternating contraction and relaxation of the hose, produced by the turning of a rotor outfitted with rollers, also called shoes.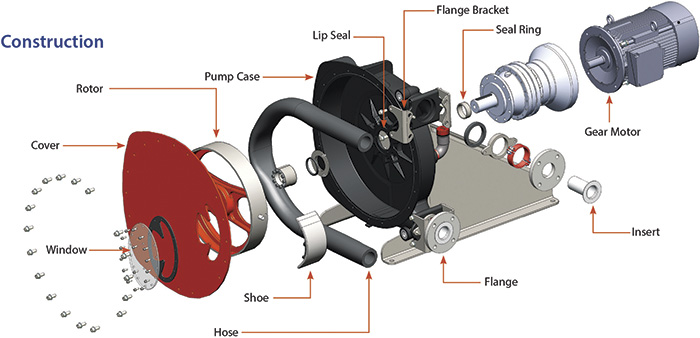 Figure 1. An example of an advanced peristaltic pump shows a seal-free design that eliminates leaks and product contamination, which enables it to handle some of the toughest pumping applications in the mining industry. (Graphics courtesy of Abaque, part of PSG)
Figure 1. An example of an advanced peristaltic pump shows a seal-free design that eliminates leaks and product contamination, which enables it to handle some of the toughest pumping applications in the mining industry. (Graphics courtesy of Abaque, part of PSG)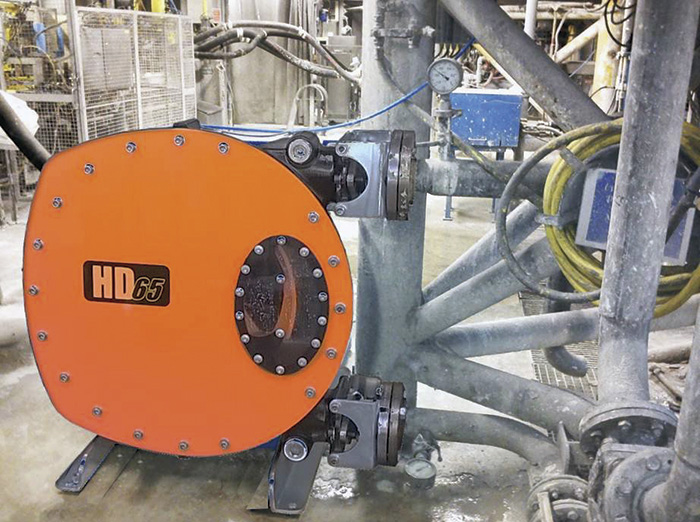 Image 1. This example of an advanced peristaltic (hose) pump designed for mining applications are constructed of heavy-duty ductile iron and stainless steel.
Image 1. This example of an advanced peristaltic (hose) pump designed for mining applications are constructed of heavy-duty ductile iron and stainless steel.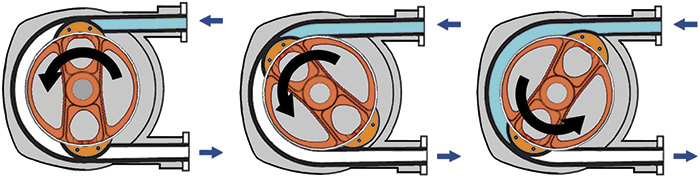 Figure 2. The design and operation of peristaltic pumps enable them to deliver a constant rate of fluid displacement and maintain high volumetric consistency, even after millions of pumping cycles.
Figure 2. The design and operation of peristaltic pumps enable them to deliver a constant rate of fluid displacement and maintain high volumetric consistency, even after millions of pumping cycles.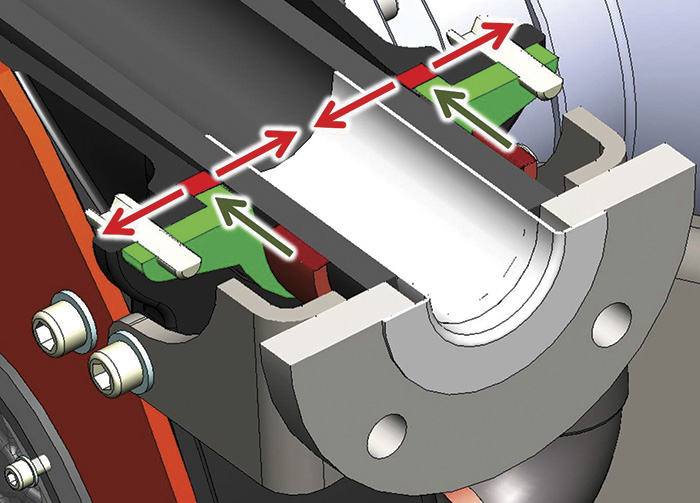 Figure 3. Advanced peristaltic (hose) pumps offer a hose holding system to provide strong hose holding and efficient tightness.
Figure 3. Advanced peristaltic (hose) pumps offer a hose holding system to provide strong hose holding and efficient tightness.- Natural rubber: Ideal for use with diluted acids and alcohols, with excellent abrasion resistance
- Ethylene propylene diene monomer: Possesses a high chemical resistance to concentrated acids, alcohols and ketones
- Hypalon: Strongly resistant to chemicals, temperature extremes and ultraviolet light
- Buna-N: Highly wear resistant to oil products
To read other Efficiency Matters articles, go here.

